Waste Water Treatment Plants
Reverse Osmosis Plant

Reverse Osmosis Plant
A reverse osmosis plant is a manufacturing plant where the process of reverse osmosis takes place. An average modern reverse osmosis plant needs six kilowatt-hours of electricity to desalinate one cubic metre of water. The process also results in an amount of salty briny waste. The challenge for these plants is to find ways to reduce energy consumption, use sustainable energy sources, improve the process of desalination and to innovate in the area of waste management to deal with the waste.
Filters

Filters
Multigrade Sand Filter
The Multigrade Sand Filter is a depth filter that makes use of coarse and fine media mixed together in a fixed proportion.
Activated Carbon Filter
Activated carbon filtration can effectively reduce certain organic compounds and chlorine in drinking water.
Softner
Water softening is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water.
Ultra Filtration

Ultra Filtration
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a type of membrane filtration in which hydrostatic pressure forces a liquid against a semipermeable membrane. A semipermeable membrane is a thin layer of material capable of separating substances when a driving force is applied across the membrane. Once considered a viable technology only for desalination, membrane processes are increasingly employed for removal of bacteria and other microorganisms, particulate material, and natural organic material, which can impart color, tastes, and odors to the water and react with disinfectants to form disinfection byproducts (DBP).
Sewage Treatment Plant

Sewage Treatment Plant
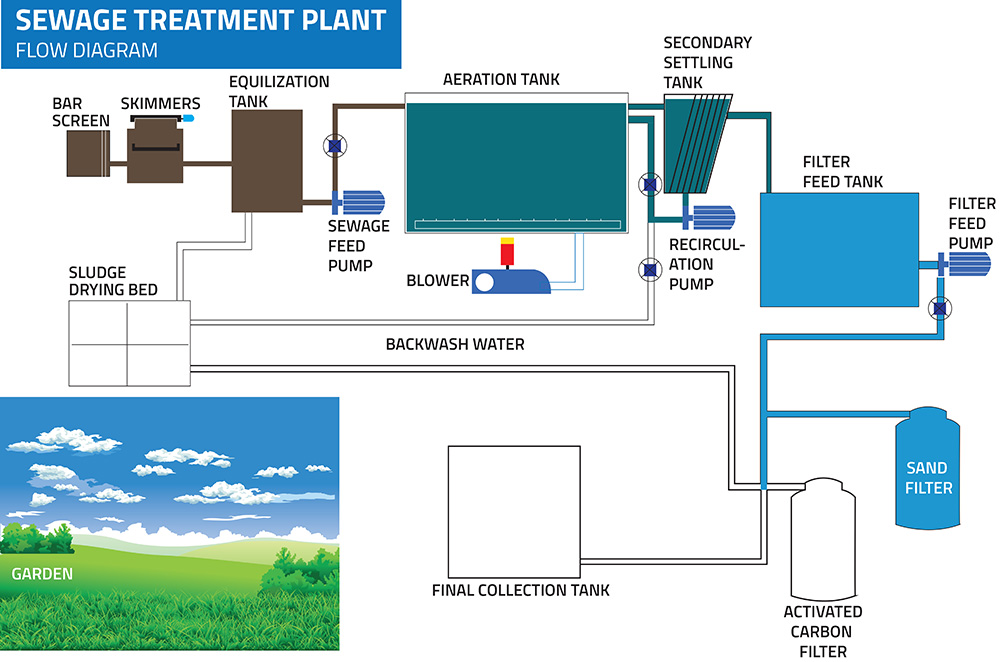
Sewage treatment is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater and household sewage, both runoff (effluents) and domestic. It includes physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove physical, chemical and biological contaminants. Its objective is to produce an environmentally safe fluid waste stream (or treated effluent) and a solid waste (or treated sludge) suitable for disposal or reuse (usually as farm fertilizer). Using advanced technology it is now possible to re-use sewage effluent for drinking water.
- E.A. (Extended Aeration)
- SAFF (Submerged Aeration Fixed Film)
- SBR (Sequential Batch Reactor)
- MBBR (Moving Bed Bio Reactor)
- MBR (Membrane Bio Reactor)
Effluent Treatment Plant

Effluent Treatment Plant
Our Effluent treatment Plants provide effective solutions to effluent odor control, BOD reduction, aeration, clarification, phosphorous and nitrogen removal and more. Our process experts work with the design team to learn the various factors that contribute to a plant’s design, including effluent requirements, land availability, energy, labor and disposal costs.
We then apply our extensive process knowledge and product expertise, analyzing the efficiency of each process, their interaction with other components, while optimizing the overall efficiency of the entire system from start to finish.
Need of ETP
- Water is basic necessity of life used for many purposes one of which is industrial use.
- Industries generally take water from rivers or lakes but they have to pay heavy taxes for that.
- So it’s necessary for them to recycle that to reduce cost and also conserve it.
- Main function of our ETP is to clean industry effluent and recycle it for further use.
